All Family MO HealthNet applicants/participants must meet and provide information regarding the following eligibility requirements under 13 CSR 40-7.015:
NOTE: Refer to Appendix A for the individual Family MO HealthNet program income guidelines which include the five percent (5%) of FPL disregard.
NOTE: RSMo 208.215 states that MO HealthNet is the payer of last resort.
13 CSR 40-7.040 states the Family Support Division (FSD) must verify all eligibility factors through available means, including information obtained through:
Except where the law requires other procedures, the FSD may accept a participant’s statement of information needed to determine the eligibility of an individual for MO HealthNet without requiring further proof from the individual, unless the FSD has information not reasonably compatible with the statement. For additional information, refer to section 1805.030.15 Reasonable Compatibility.
If verification cannot be obtained by the FSD through electronic data sources or if the information is not reasonably compatible with collected information, the FSD must ask for any additional information by sending a Request for Information (IM-31A) to the participant.
The participant must provide the required verification within ten (10) days from the date that the FSD requests the information in writing. A participant may request additional time to provide the information. The additional time shall be granted if the participant is making a reasonable effort to obtain the information.
NOTE: Only one IM-31A is required to be sent.
If a participant fails to provide the requested verification within ten (10) days from the date of the written request or fails to obtain additional time to provide the information, the division must:
Comments on the case must support all information requested and additional time granted.
The FSD will only accept an applicant’s/participant’s statement from the following:
NOTE: Verification of Social Security Number (SSN), Identity, Citizenship, Immigrant status, and Income are required by law.
Comments on the case must support what was used to verify eligibility factors.
Federal Hub Calls (H-calls) are the electronic services provided by the Secretary of Health and Human Services, which States may use to verify or obtain certain information, 42 CFR 435.949.
H-calls are used by the Marketplace and States to obtain information provided by Federal Agencies, Social Security Administration (SSA), the Department of Treasury, the Department of Homeland Security and other data sources.
H-calls lessen the burden of requiring households to provide verification. Because of H-call and other electronic sources, the individual does not have to provide the same verification(s) to multiple agencies.
NOTE: Family Support Division (FSD) must check the electronic data sources to obtain information regarding the individual or household’s circumstances whenever possible.
As conditions of eligibility, all individuals seeking MO HealthNet (MHN) must provide and verify their Social Security Number, Citizenship and Immigration Status. H-calls should be used instead of requesting the individual to provide the documentation. H-calls can provide the following information:
Individuals must not be required to provide additional information or documentation unless electronic data sources cannot provide the information required to determine eligibility. When information received from H-calls or other electronic data source cannot be used to determine eligibility, clarification should be requested. Clarification should be requested when:
NOTE: MAGI Policy manual section 1805.030.15 Reasonable Compatibility explains how to treat income that is not compatible.
EXAMPLE: Xavier attested that he is a lawful permanent resident and has been in the United States legally for over five years. The H-call for citizenship returned conflicting information; it showed that Xavier has only been in the United States for three years. Xavier must have been in the United States legally for five years to receive MHN benefits. An IM-31A Request for Information is sent to Xavier requesting he provide clarifying documentation regarding his immigration status.
In the event that H-call services are down and not working, or an error or no response is received, and other electronic data sources cannot provide the information, request the individual provide the required information.
Reasonable opportunity applies to the 90 day period participants are given to provide:
NOTE: Section 6036 of the Deficit Reduction Act of 2005 (DRA) states that when documentation of citizenship includes proof of identity, the application may be approved pending documentation of citizenship even when proof of identity has not been provided. Do not provide a reasonable opportunity period for verification of identity only.
Section 1902(a) of the Social Security Act requires individuals to apply for and provide a Social Security Number (SSN) as a condition of eligibility for MO HealthNet. See 1805.015.00 SOCIAL SECURITY NUMBER for exceptions.
Allow reasonable opportunity for persons requesting benefits who do not have citizenship documents/proof of qualified immigrant status or a SSN at the time of application.
Reasonable opportunity for SSN is only allowed when proof of application for a SSN is provided. Reasonable opportunity for SSN is not given if:
NOTE: If the application for SSN is for employment authorization only, they may receive the RO period.
When an applicant does not already have a SSN at the time of the Family MO HealthNet application:
NOTE: Under 42 CFR 435.910, FSD staff must assist applicants in obtaining a SSN. Refer to 1805.015.00 SOCIAL SECURITY NUMBER for more information.
NOTE: The 90 day reasonable opportunity period begins the day the MO Health Net application is approved.
Example: Ms. Jones states on her Family MO HealthNet application that she does not have a SSN. A Request for Information notice is sent to Ms. Jones to request proof of application for a SSN. Ms. Jones submits verification that she has filed for a SSN. She is eligible on all other factors and is approved for coverage. She is given a 90 day reasonable opportunity period to provide the SSN.
Section 6036 of the DRA requires individuals claiming U.S. citizenship or qualified immigrant status to provide satisfactory documentary evidence of citizenship or nationality when applying for MO HealthNet. Refer to MAGI Manual section 1805.020.05.05 Documents to Verify Citizenship for information on acceptable citizenship documentation. Refer to MAGI Manual section 1805.020.10 Qualified Immigrant for information on persons with qualified immigrant status.
Applicants for Family MO HealthNet must declare under penalty of perjury that they are citizens or qualified immigrants on a document that explains the penalties under state law for obtaining public assistance benefits fraudulently. The signed application serves as this declaration. RSMo. 208.009 states that an applicant who cannot provide proof of citizenship or qualified immigrant status at the time of application may be given a reasonable opportunity to provide the information if:NOTE: Social Security Numbers issued to non-citizens are allowable since the individual may have qualified immigrant status. If a participant provides a SSN, but does NOT claim citizenship or qualified immigrant status, do NOT pend the application for citizenship/qualified immigrant status and do NOT provide a 90 day reasonable opportunity period.
NOTE: When waiting on a birth certificate, staff must still review the case in ninety (90) days and then provide 30 day extensions of the reasonable opportunity period as needed.
When an applicant does not provide a SSN, other federal identification number, or citizenship documents/proof of qualified immigrant status at the time of the Family MO HealthNet application:
NOTE: Self-attestation of SSN or applicable federal identification number is acceptable to provide the reasonable opportunity period. If an applicant declares citizenship status, but does not have a SSN or citizenship documentation, FSD must assist the participant in applying for a SSN (see 1805.015.00 SOCIAL SECURITY NUMBER). If the participant is submitting a birth certificate, they must provide verification that they have applied for it in order to receive reasonable opportunity.
Example: Ms. Jones applies for Family MO HealthNet coverage as a qualified immigrant, but does not include a SSN or applicable federal identification number on her application. A Request for Information notice is sent to Ms. Jones to request SSN, applicable federal identification number, and qualified immigrant documents. Ms. Jones submits her alien identification number, but not her supporting documents. She is eligible on all other factors and is approved for coverage. She is given a 90 day reasonable opportunity period to provide the qualified immigrant documents.
NOTE: The 90 day reasonable opportunity period begins the day the MO Health Net application is approved. If proof of application for SSN is received, staff may approve the application and provide a 90 day reasonable opportunity period for both citizenship and SSN concurrently.
NOTE: The reasonable opportunity period may be extended beyond the 90 day period if a participant is making a good faith effort to provide verification of citizenship or qualified immigration status.
If documentation has not been provided within 90 days:
If the participant responds before the expiration of the Adverse Action Notice, but does not have citizenship documentation or proof of qualified immigrant status:
EXAMPLE: Ms. Jenkins did not provide documentation of qualified immigrant status when she applied for Family MO HealthNet. She supplied her applicable federal identification number, was found eligible on all other factors, was approved for coverage, and was given 90 days to provide verification of qualified immigrant status on 8/10/2016. The 90 reasonable opportunity period ends in November 2016.
Ms. Jenkins fails to provide documentation of qualified immigrant status by November. The Eligibility Specialist sends Ms. Jenkins an Adverse Action Notice (IM-80) to discontinue MO HealthNet coverage. Before the expiration of the Adverse Action Notice, Ms. Jenkins provides a letter from the United States Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS) explaining the paperwork delay. The Eligibility Specialist, with supervisor approval, voids the adverse action, and sends a new Request for Information providing Ms. Jenkins with a 30 day extension of the reasonable opportunity period.
Approval notices for Family MO HealthNet benefits approved with a reasonable period must state that the participant’s continued eligibility is contingent on the provision of SSN or verification of citizenship/qualified immigrant status.>
An individual may reapply for MAGI coverage after being closed for not providing citizenship documents and/or Social Security Number (SSN) within the 90 day reasonable opportunity period. However, the individual cannot receive an additional 90 day reasonable opportunity period after coverage has closed for failure to provide citizenship/SSN information.
NOTE: It is important to note that while a participant must provide documentation of citizenship or immigrant status, he or she only needs to provide FSD with the Social Security Number, NOT a copy of the Social Security card.
If coverage ended after the 90 day reasonable opportunity period because the individual failed to provide citizenship and/or SSN information, do not authorize another 90 day reasonable opportunity period. The applicant is given a Request for Information allowing the applicant ten days to provide the information. If the information is not provided the application is rejected.
Example: On 07/23/2016, Ms. Smith's application was approved with 90 day reasonable opportunity. She must provide citizenship documentation for herself and her three children. Ms. Smith fails to provide the passports or any other citizenship documentation within 90 days and does not contact FSD claiming a good faith effort in submitting the information. An Adverse Action notice is sent, and when it expires, the MAGI case closes and an Action Notice is sent to Ms. Smith. On 12/23/16, Ms. Smith reapplies for herself and her three children. Again, Ms. Smith does not provide verification of citizenship for herself or her children. Ms. Smith is given the Request for Information allowing her 10 days to provide citizenship documentation. Ms. Smith fails to provide verification of citizenship at the end of the 10 day period and therefore, her application rejects.
42 CFR subsection 435.403 requires individuals to reside in the state where they are applying for benefits. The residence requirement is verified through self-attestation.
A participant’s statement of an individual’s age, date of birth, and household size is acceptable verification.
Section 1902(a) of the Social Security Act requires individuals to apply for and provide a Social Security Number (SSN) as a condition of eligibility for MO HealthNet.
Note: This requirement applies only to those persons requesting or receiving MO HealthNet benefits. It does not apply to parents or children included in the household who are not requesting benefits.
Obtain a SSN for all individuals including children under one requesting benefits at the time of the initial application whenever possible. Accept self-attestation for verification of SSN.
EXCEPTION: An exception may be given to applicants who do not have, or do not agree to apply for, a SSN due to a well-established religious belief. A well-established religious belief means that the applicant is a member of and abides by the belief of the religious organization. Self-attestation is accepted unless it is questionable.
If an individual has a SSN but does not know it, provide a Request for Information (IM-31A) and allow ten days to provide the SSN.
Note:When an individual attests to having a SSN but fails to provide it to FSD, the individual should be rejected after the IM-31A Request for Information expires. Do not allow Reasonable Opportunity (RO) in this situation.
If the individual does not have a SSN, s/he must agree to apply for a number at the Social Security Administration (SSA) Office. FSD will assist the individual in making an application for SSN.
Note: FSD should assist in completing the SS-5 and mailing it to the SSA Office whenever necessary. The applying individual MUST sign the SS-5 prior to being submitted to the SSA Office.
Note: Whenever the completed SS-5 form is mailed to the SSA Office by FSD on behalf of the individual applying for a SSN, provide the individual with a copy of the completed SS-5 prior to mailing it to the SSA Office.
Note: Inform the individual the SSA Office requires, and may request from them, original documents (i.e. birth certificate, marriage certificate, etc.) when making application for a SSN.
Note:To find local Social Security Office for the individual applying for a SSN go to the Social Security website and utilize the Social Security Office Locator tool. Use this tool when determining which office to direct the individual or to mail the SS-5 for the individual.
Enter a comment providing details on how the FSD assisted with the application for SSN, when the SSN application was made, etc.
Allow reasonable opportunity for persons requesting benefits who do not have a SSN. Refer to manual section 1805.000.05 Reasonable Opportunity.
Note: The application for SSN from the Social Security Administration office must be received prior to allowing the 90 day Reasonable Opportunity period. Providing the individual with the SS-5 does not meet the requirement for proof of application for SSN, nor does a SS-5 completed by the individual. The individual must provide proof that they have made application through the Social Security Administration Office.
Missouri Rule 13 CSR 40-2.260 provides that Newborns born to women with active Title XIX coverage at the time of the baby’s birth continue to be eligible for Newborn coverage up to age one whether or not they have a SSN on file with FSD.
Note: Review MAGI Manual 1860.010.00 Eligibility for a list of MHN Programs that are Title XIX.
Within 60 days of Newborns (babies born to women actively receiving Title XIX coverage on the baby’s date of birth) turning one year old, a review of their coverage will be completed. Any missing case information, along with SSN, should be obtained at that time.
Note: The 90 day Reasonable Opportunity (RO) period does not apply to Newborns during their first year of life when born to women born with Title XIX coverage at the baby’s birth. These babies are automatically eligible from the date of birth until their first birthday regardless if the FSD has been provided with the baby’s SSN.
When FSD has not been provided with the Newborn’s SSN by the baby’s first birthday, send an IM-31A requesting the SSN. If the SSN is not provided, the baby cannot continue to receive any MO HealthNet programs after the first birthday.
If application for a SSN has been made for the Newborn, but the participant has not yet received the SSN by the baby’s first birthday, give the participant the 90 day RO period to supply the number.
Applications for children under age 1 (MHK under 1) whose mother was not active Title XIX coverage on the baby’s date of birth are not automatically eligible for Newborn coverage during the first year of life. Request the baby’s SSN by sending the IM-31A when processing the application for MHK under 1.
Note: The 90 day RO period may be allowed if the application for the baby’s SSN has been made but not received by the family. Request proof of the application for the baby’s SSN by sending the IM-31A. Once proof is provided, allow the 90 day RO period.
Refer to MAGI Manual section, 1805.000.05 Reasonable Opportunity.
Individuals failing to complete an application for a SSN or failing to provide an existing SSN are not eligible for MO HealthNet. Include their needs and income in the budget when determining eligibility for the remaining members.
When processing applications which include individuals who have not applied for a SSN or who have not provided an existing number:
EXCEPTIONS: Newborn children who are automatically MO HealthNet eligible may receive for one year without providing verification of a social security number.
NOTE: If there is non-compliant individual is the only child in the home, the caretakers do not qualify for MO HealthNet for Families (MHF).
Individuals denied due to failure to apply for, or disclose an existing SSN must verify they have complied to be eligible. Individuals who were denied can become eligible no earlier than the first day of the prior quarter preceding the date they comply.
Determine cooperation on this factor at each review.
Section 6036 of the Deficit Reduction Act of 2005 amended section 1903 of the Social Security Act to require states to obtain satisfactory documentation of citizenship and identity prior to approving MO HealthNet benefits, effective July 1, 2006.
Individuals exempt from providing documentation of citizenship and identity are listed in Section 1805.020.05.
Section 1805.020.15 lists acceptable documents to use as verification.
Section 211 of the Children’s Health Insurance Program Reauthorization Act (CHIPRA) signed February 4, 2009, amended section 1903(x) of the Social Security Act. The law allows an individual declaring to be a citizen or national of the United States who is required to present documentary evidence of citizenship or nationality a reasonable opportunity to present the documentation. The reasonable opportunity period is defined as 90 days from the date of approval. Refer to section 1805.000.05 Reasonable Opportunity for more information.
The Personal Responsibility and Work Opportunity Reconciliation Act (PRWORA) of 1996 changed eligibility for individuals who are not citizens of the United States. MO HealthNet eligibility for immigrants is based on:
Effective July 1, 2006, states must obtain documents establishing citizenship and identity for new applicants and participants for all categories of MO HealthNet. Individuals are exempt from the requirement when he or she receives at least one of the following:
NOTE: For immigrants from Micronesia, Palau, and the Marshall Islands, refer to Section 1805.020.10.30
42 CFR §435.407 and §436.407 describe the documents needed to verify citizenship and identity.
NOTE: As of January 20, 2017, a photocopy, facsimile, scanned or other copy of a document must be accepted to the same extent as an original document under this section, unless information on the copy submitted is inconsistent with other information available to the agency or the agency otherwise has reason to question the validity of, or the information in, the document.
Acceptable forms of documentation that verify both citizenship and identity are:
NOTE: MODL cannot be used to verify relationships as it does not capture coding details for why a name has been changed.
Staff will need to check with the issuing state to verify the state’s process.
NOTE: A verified SSN is NOT a verification of citizenship. Citizenship may be verified through a Bendex, SDX or IIVE alien indicator. Refer to the CITIZENSHIP DOCUMENT ENTRY FOR APPLICATIONS guide in MEDES Resources for more information.
NOTE: The documents listed above may include, but are not limited to:
NOTE: In Missouri, LOC of "G" (newborn coverage) on the MXIX screen verifies this factor.
If one of the above forms is not available, you must obtain one of the following documents to verify citizenship and a second source to verify identity. The following documents may be used to identify citizenship for MAGI programs:
NOTE: Evidence of birth in Puerto Rico and the applicant's statement that he or she was residing in the U.S., a U.S. possession, or Puerto Rico on January 13, 1941 is acceptable.
NOTE: Do NOT print IBTH screens or file in the case record
NOTE: MEDES verifies a participant’s citizenship and immigration status by:
FSD must accept the following as proof of identity for MAGI cases, provided such document has a photograph or other identifying information sufficient to establish identity, including, but not limited to, name, age, sex, race, height, weight, eye color, or address:
NOTE: Do not request verification of identity again when the child turns 16 years old as long as there is continuous eligibility for that child and there is the prior affidavit signature of the parent/related caretaker/legal guardian.
FSD may rely, without further documentation of citizenship or identity, on a verification of citizenship made by a Federal agency or another State agency, if such verification was done on or after July 1, 2006.
FSD must provide assistance to individuals who need assistance in securing satisfactory documentary evidence of citizenship in a timely manner. If the individual is unable to obtain documentation listed above for either citizenship or identity, contact the MHN Program and Policy Unit for further assistance.
A qualified immigrant is one who is:
All qualified immigrants who were in the U.S. PRIOR to August 22, 1996, and who otherwise meet MO HealthNet eligibility criteria, are eligible.
Qualified immigrants entering the U.S. ON OR AFTER August 22, 1996, may be eligible for MO HealthNet immediately, or may be subject to a five-year period of ineligibility.
Qualified immigrants entering the U.S. on or after August 22, 1996 who are members of one of the groups listed below have no waiting period:
Qualified immigrants entering the U.S. on or after August 22, 1996 who are not eligible for MO HealthNet for five years following their date of entry are listed below. Once the five-year period of ineligibility has expired, these qualified immigrants who otherwise meet MO HealthNet eligibility criteria can receive MO HealthNet:
EXCEPTION: The five-year ineligibility period DOES NOT APPLY to the immigrants listed above if they are:
NOTE: Qualified immigrants subject to the five-year period of ineligibility may be eligible for emergency medical care for ineligible immigrants, see Income Maintenance Manual section 1700.000.00 Emergency MO HealthNet Care for Ineligible Aliens (EMCIA)
Non-qualified immigrants are ineligible for MO HealthNet benefits.
NOTE: Non-qualified immigrants may be eligible for emergency medical care for ineligible immigrants, see Income Maintenance Manual section 1700.000.00 Emergency MO HealthNet Care for Ineligible Aliens (EMCIA).
Immigrants from Micronesia, Palau and the Marshall Islands have signed a Compact of Free Association with the United States, which allows them to enter and leave the U.S. at will. These individuals are not eligible to receive MO HealthNet benefits unless they apply for immigrant status with the United States Citizenship and Immigration Service (USCIS - formerly Immigration and Naturalization Service) and are given a qualified immigrant status. Immigrants with a qualified status may be eligible for MO HealthNet benefits if all eligibility criteria are met.
All non-citizen applicants for MO HealthNet who declare they are qualified immigrants must provide Department of Homeland Security (DHS) documents to establish immigration status.
If the applicant provides the requested documentation, verify the documentation with the DHS using the SAVE System.
NOTE: MEDES verifies a participant’s citizenship and immigration status by:
EXCEPTION: The DHS SAVE system does not contain information about victims of severe forms of trafficking. Until further notice, do not contact SAVE concerning these individuals. See Income Maintenance Manual section 1510.020.00 for more information on victims of trafficking.
If the applicant presents an expired DHS document or is unable to present any documentation of his or her immigration status, refer the person to the local DHS District Office to obtain evidence of status unless he or she can provide an immigrant registration number.
If the applicant provides documentation with an immigrant registration number, use the VLP Scan and Upload process to send documentation to the DHS to verify immigration status. DHS will determine the authenticity of the document and determine whether immigration status is met. If the applicant presents verification he or she has applied to DHS for a replacement document, contact the DHS to verify status by using the SAVE System.
When verification of qualified immigrant status is not available through paper documentation when Step 3 is triggered, and the individual meets all other eligibility requirements, approve the MO HealthNet application based on the applicant’s statement. A period of 90 days from the date of approval is allowed as a reasonable opportunity to provide documentary evidence for individuals stating they are lawfully present in the United States and:
See Income Maintenance Manual sections 1805.020.10.10.05 and 1805.020.10.10.10 for policy on the five year ineligibility period and exceptions to the five year period of ineligibility.
If requested verification is not provided within 90 days, close the applicant’s benefits by manually sending a Notice of Adverse Action (IM-80) using the code CTV- failed to provide citizenship/alien documentation. At the end of the IM-80 period, manually send a Case Action Notice (IM-33C) using the CTV code and send an e-mail to the Cole.MHNPolicy@dss.mo.gov for a Program Development Specialist (PDS) to enter an override to end the individuals MO HealthNet benefit.
Each office must manually track the 90 day reasonable opportunity period using the same method offices use today for tracking citizenship reasonable opportunity periods.
Acceptable documentation of qualified immigrant status:
| Immigration Status | Verification Document (Department of Homeland Security (DHS) U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS) forms unless otherwise noted. Access the Systematic Alien Verification for Entitlements (SAVE) database to verify USCIS documents.) |
|---|---|
| Lawful Permanent Resident (LPR) |
|
| Refugees |
|
| Asylee |
|
| Afghan Special Immigrants | Refer to Documentation for Special Immigrants chart |
| Iraqi Special Immigrants | Refer to Documentation for Special Immigrants chart |
| Immigrant with Deportation or Removal Withheld |
|
| Immigrant Granted Parole for at Least One Year |
|
| Immigrant Granted Conditional Entry |
|
| Cubans and Haitians |
|
| Battered Immigrant |
|
| American Indian born in Canada (Cross-border Native American) |
|
| Amerasian Immigrant |
|
| Trafficking Victim |
|
| U.S. Military Veteran |
|
| U.S. Military Active Duty Personnel (Army, Air Force, Marine Corp, or Coast Guard) |
|
| Spouse, Unmarried Surviving Spouse ,or Child of a Veteran or Active Duty Armed Forces Military |
|
A participant’s statement of pregnancy is acceptable verification of pregnancy and estimated due date, unless the agency has information that is not reasonably compatible with the participant’s statement.
The Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (PPACA or ACA), effective January 1, 2014, introduced the Modified Adjusted Gross Income (MAGI) methodology. MAGI is a methodology for determining MO HealthNet eligibility based on federal income tax filing rules for income and family size.
These income eligibility rules will apply to all participants eligible for the following MO HealthNet programs:
NOTE: The Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (PPACA or ACA) does not change MO HealthNet eligibility rules for participants who are 65 years of age or older or those in eligibility categories based on disability.
Income is verified by self-attestation. Self-attested income that is countable within the MAGI budget must be confirmed, see 1805.030.20.05 Income Included Under MAGI.
Confirmation of Self-Attested Income
Electronic data source income information should be used first to confirm the income whenever possible.
For self-attested income to be considered confirmed, the income should meet criteria in one of the following bullets. Apply the following order when confirming income.
Electronic Data Sources
If information is available from the electronic data sources the agency must obtain the electronic data information before attempting to confirm the income any other way (i.e. clarifying statement, or income documentation).
Available electronic data sources must be used in the following order prior to requesting clarification or income documentation from the individual.
NOTE: The individual must give the FSD permission to access the Federal Data Hub. This is usually done on the filer consent when the individual signs the paper application or when the individual submits an online application. The permission is given to the FSD to access Federal Data Hub information for a period of time, 0 to 5 years, as determined by the individual.
NOTE: IRS information received from the Federal Data Hub cannot be printed, saved or stored. The information can only be viewed.
NOTE: When determining current and ongoing eligibility, the Work Number is used as an electronic data source. If the self-attested amount is not Reasonably Compatible (RC) with the electronic data sources (including The Work Number), clarification of income should be requested.
When determining eligibility in Prior Quarter (PQ) months, information provided by The Work Number can be used as income verification.
NOTE: New Hire Matches and Quarterly Wage Matches can only be used as income verification if the participant has reported the source of income, and the information is reasonably compatible.
Store the electronic data source income information (excluding IRS information) in the Virtual File Room.
Requesting Income documentation:
When the electronic data source and reasonable statement request fails, it is appropriate to requested income documentation. Only request documentation of self-attested income when:
Request the previous 30 days of pay history. If the previous 30 days does not accurately reflect a projection of ongoing income request further pay history to accurately project income. See MAGI Policy Manual, 1805.030.25.05 Projection of Income.
NOTE: Pay history from the past 30 days may not accurately reflect a projection of ongoing income when the individual is a seasonal worker, income includes overtime, the individual was on leave without pay, the individual started or stopped a job, etc.
Employer or Income Source Discrepancies
If the individual has not reported an employer or income source, and the electronic data source has information of an employer or income source, contact the participant for clarification.
When self-attestation of an employer or income source is different than what is received from the electronic data source or different from information in our records, determine if the sources and income are compatible.
NOTE: If our records indicate a different employer/income source than what is self-attested, do not request verification that the income source in our records has ended unless it is questionable or not compatible. End the income source in our records based on self-attestation.
The sources are considered compatible when; income from both meets the guidelines for Reasonable Compatibility, and the employer or income sources are similar. If the sources and income are compatible accept self-attestation, if they are not compatible request clarification.
EXAMPLE: James reports he works at Wal-Mart and earns $8.25 per hour and works 32 hours per week. James' self-attested income would be equal to $1,143.65 per month (32 x 2 = 64 x $8.25 = $528.00 x 2.166 = $1,143.65/month). With James' income and household size he falls within MHK category of 148% of the FPL. The electronic data source income shows James is employed at Target and earns $900 per month, which is within the MHK category as well. The income sources and income amounts are similar therefore no further information is needed.
Zero Income
Income of individuals or households attesting zero income must be confirmed. Treat self-attestation of no income the same as self-attestation of income.
When zero income is attested and:
When income is attested and:
Modified Adjusted Gross Income (MAGI) methodology uses federal tax filing status to determine the household composition. Individuals on the same case or application may have different household compositions than other individuals in their household.
It must be first be determined if the individual expects to file taxes or expects to be claimed as a dependent before applying tax filer rules or non-filer rules. Self-attestation is accepted for tax filing status/tax filing relationships.
NOTE: When the tax filing status is unknown or questionable, send an IM-31A to request clarification of the expected tax filing status and tax relationships. If the individual fails to provide the requested clarification, reject/close the case/application for Failure to Cooperate.
Tax filer rules apply if the individual intends to file a federal income tax return or be claimed as a dependent on a federal income tax return for the year coverage is requested;. When the individual attests to being a filer or a dependent on a federal tax return, apply tax filer rules even when the individual is not required to file, and regardless of whether the tax return is actually filed.
Non-filer rules apply when the individual does not plan to file a federal income tax return and does not expect to be claimed as a tax dependent on a federal income tax return for the year coverage is requested.
Tax dependents are normally part of the tax-filer’s household with some exceptions: refer to manual section, 1805.030.10.20 Exceptions to MAGI Household Composition.
Effective January 1, 2014, the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (PPACA or ACA) of March 2010 requires household composition to be determined using Modified Adjusted Gross Income (MAGI) methodologies per 42 CFR 435.603 (f).
For tax filing households, the tax filer and individuals to be claimed as dependents on a taxpayer’s federal income tax return are included when determining household size, (with some exceptions).
The household for a tax filer consists of the following individuals:
The household of the tax dependent is the same as the tax filer’s household; unless the tax dependent meets one of the exceptions in 1805.030.10.20 Exceptions to MAGI Household Composition. When a tax dependent meets an exception, non-tax filer rules apply.
Exception: For Family MO HealthNet programs, a “Child” or “Children” means a person or persons who are under nineteen (19) years of age” under 13 CSR 40-7.010(B). Therefore, the parents of a person under age 19 must be included in the household composition and the parents’ income is counted even if the child claims he is a non-dependent tax filer. These individuals fall under non-filer rules because they are children who are not claimed as tax dependents.
Household composition based on non-tax filer rules includes family members who live with the individual. Non-tax filer households include the following:
Apply non-tax filer rules if the individual meets any of the following exceptions:
EXAMPLE ONE: Mom and Dad, not married, both over age 19, live together, and have a child (age 3). Mom and Dad each file taxes separately. Dad claims their child as his tax dependent. The MAGI households for each applicant would be as follows:
EXAMPLE TWO: Mom and Dad, not married, both over age 19, live together, and have a child (age 3). Mom is a non-tax filer and Dad is a tax filer. Dad claims their child as his tax dependent. The MAGI households for each applicant would be as follows:
EXAMPLE THREE: Grandmother and two granddaughters (both under age 19 and sisters) live together. Grandmother is a non-tax filer. The households for each applicant would be as follows:
True joint 50/50 custody occurs when the child(ren) spend an equal number of overnight visits with each parent. Per Missouri Rule 13 CSR 40-7.010 the non-custodial parent is defined as the parent who does not have physical custody of the child.
The parent with whom the child spends more than 50% of their overnight visits with is considered to be the parent exercising the majority of the child’s care and control and therefore is the custodial parent regardless of tax filing status.
NOTE: 42 CFR 435.4 provides that parents must reside in the home of the eligible child(ren) in order for the parent to be eligible for MAGI MO HealthNet for Families (MHF).
NOTE: Parents who claim the child(ren) as a tax dependent but do not practice true 50/50 joint custody (they have the child(ren) less than 50% of the time) are not eligible for MHF due to ineligible living arrangements.
EXAMPLE: John and Linda have a divorce decree stating they have joint physical custody of their child, Lauren. John claims Lauren as a tax dependent on his taxes. Linda applied for benefits on Lauren. Linda states she has Lauren more than 50% of the time. Linda provided a revised parenting plan, signed by John and Linda, which states Lauren stays with Linda 4 nights per week. Lauren is physically with Linda more than she is with John, therefore Linda may apply for benefits for Lauren.
The custodial parent must carry health care coverage for the child. The custodial parent is the parent that applies for MO HealthNet (MHN) benefits.
EXAMPLE: Mom and dad exercise true 50/50 joint custody, dad claims the child as a tax dependent each year and must carry coverage for the child. Mom is a tax filer but does not claim any dependents and does not have any other household members. Mom applies for MHF coverage on herself and reports the child in her home 50% of the time. Mom does not qualify for MHF because she is the non-custodial parent. The mom's household size is one: herself. The child's household size is two: the child and dad.
If the custodial parent is in question, follow the steps below to determine which parent is considered the custodial parent for the purpose of making a MHN application.
NOTE: It may be necessary to count the overnight stays with each parent to determine where the child is more often.
NOTE: It may be necessary to count the overnight stays with each parent to determine where the child is more often.
NOTE: If the parents alternate each year claiming the children as part of their tax filing household, the non-custodial parent is considered the parent who does not plan to claim the child as a tax dependent for the period MHN benefits are being requested. The parents must alternate years they each apply for MHN for the child.
Refer to the Household Composition Flow Chart to help determine household composition.
Caretaker relatives are an exception to the MAGI Household Composition. Caretaker relatives can make application for a dependent child and themselves if the caretaker relative is assuming primary responsibility of the child. The caretaker relative must meet income guidelines for MHN.
Claiming the child as a tax dependent can demonstrate an assumption of primary responsibility, however it is not the sole determining factor. A caretaker relative must live in the same household as the dependent child, assume primary responsibility, and be related to the dependent child.
NOTE: The caretaker relative assuming primary responsibility of the child does not have to be claiming the child as a tax dependent.
A caretaker relative relationship can be defined as the child's parent, or as:
NOTE: Caretaker relatives by marriage are still to be included even if the marriage has been terminated, either by death or divorce. The caretaker relative must be assuming primary responsibility for the dependent child as defined above.
EXAMPLE: Jon lives with, and is the uncle to, Gavin, age 10. Jon is the caretaker relative to Gavin. Jon is not a tax filer and Gavin is not expected to be claimed as a tax dependent by anyone else. Jon applies for MHN for himself and Gavin. Jon's MAGI household size is 1 for himself and Gavin's MAGI household is 1 for himself. Non-tax filer rules apply for the dependent child.
The tax filer of the dependent child may reside in the same home as the caretaker relative and the dependent child, when the tax dependent child is an in-common child of the tax filer and the caretaker relative.
EXAMPLE: Melissa applied for MHN for herself and her two children. She lives with the father of her children but she is not married to the father. The father claims the children as tax dependents. Melissa does not work and does not file taxes. Melissa’s household would follow non-tax filer rules. She would be eligible for MHF as a household size of 3 (herself and two children), if all other eligible criteria are met. The children’s household size is four: the two children, the mother and the father.
Client's statement is acceptable when a person is claiming to be a caretaker relative of a child. If the situation is questionable or if the tax filer disputes the caretaker relative's statement, request further documentation.
IM-#39 March 15, 2019, IM-#96 July 13, 2017, IM-46 May, 12, 2017, IM-7 January, 27, 2017, IM-#97, November 9, 2015
Reasonable Compatibility (RC) is defined as the allowable difference between the self-attested income and the income reported by the Electronic Data Sources (EOI).
RC is used to confirm the self-attestation of income. When the self-attested income is not RC with the EOI further clarification is required from the individual to substantiate the self-attested income.
NOTE: RC’s primary purpose is to determine if further clarification should be requested from the individual. When the income is not RC, the EOI returns no response or an error, or when the self-attested/EOI information is questionable; further clarification should be requested.
Income is considered RC when:
OR
NOTE: The eligibility determination is based on the self-attested income. Neither RC nor the EOI are used to make an eligibility determination.
Income is NOT considered RC when:
NOTE: Whether the difference is within 10% or not, income is not considered RC and additional verification will need to be requested.
Whenever there is a Change in Circumstance (CIC) that affects the budget, RC should be applied to determine if further clarification is needed from the individual. RC should be applied in the following situations, as appropriate:
When self-attestation of the employer, or the income source, is different than what is received from the EOI, determine if the sources are compatible. The sources are considered compatible when:
If the employers/income sources are compatible accept self-attestation for the income source.
NOTE: If our records indicate a different employer/income source than what is self-attested, and the employers/income sources are compatible, do not request verification that the income source in our records has ended. It is appropriate to accept self-attestation in this situation.
Paystubs are considered the individual's self-attestation and the verification of income. Paystubs trump the information returned by an EOI when there are discrepancies. Use the pay stubs as verified income evidence.
EXAMPLE: Sue provided her weekly pay stubs for the past 4 weeks with her application. Her pay stubs are used as Sue's attestation and verification of her income. With Sue's pay stubs/self-attestation, Sue's income is below the eligibility threshold for MHK (148% of FPL). The EOI shows income above the eligibility threshold for MHK and more than 10% difference from the pay stubs.
Outcome: Based on her self-attestation, Sue is MHK eligible. RC does not need to be explored as the pay stubs are considered verified and reflect information more recent than the EOI.
When pay stubs are provided, RC does not need to be completed.
Explore RC with all available EOI before requesting additional information/clarification from the individual.
To determine if the income is RC gather the following information:
The MO HealthNet program thresholds are grouped together as listed below.
NOTE: RC should be applied to each CHIP category (CHIP 71/72, CHIP 73, CHIP 74, and CHIP 75) separately.
The income is considered RC when the self-attested income falls below the MO Health Net program income threshold and EOI falls above, and the EOI is within 10% of the self-attested amount. This is called the 10% Reasonable Compatibility Test.
To apply the 10% RC Test, complete the following steps for each individual in the household with income:
NOTE: MO HealthNet eligibility is determined for each individual by the individual's household size and applicable income. Since households are determined by the tax filing unit, each person in the household could potentially have a different household size.
If the self-attested income is below the threshold and the electronic data source income are within 10% of each other, the individual's income is reasonably compatible. Use the self-attested income for the budget and eligibility determination.
OR
If the self-attested income is below the threshold and the EOI is above but not within 10% of each other, or the self-attested income is above the threshold while the EOI is below, or the self-attested income and the EOI fall in different MO HealthNet program thresholds, the individual's income is not reasonably compatible. Request a reasonable explanation to clarify the difference between the self-attested income and the electronic data source income.
OR
If a reasonable explanation is not given or the explanation given is not reasonable, request further verification.
EXAMPLE: George self-attested his income at within the MHK threshold (148% of the FPL), the electronic data source income for George was within CHIP 71 threshold (150% of the FPL), but his self-attested income and the electronic data income was within 10% of each other. George's income is reasonably compatible. He would be eligible at the MHK category level based on his self-attestation.
NOTE: When applying the 10% Reasonable Compatibility Test and one of the household member's income passes the 10% Reasonable Compatibility Test and another household member's income fails, only request a reasonable explanation/clarification for the income that failed the test.
| Attested Income | Electronic Data Source | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Is below the income eligibility threshold. | Is below the eligibility threshold. | Self-attested income is used. Individual is eligible. 10% Reasonable Compatibility Test is not required. |
| Is below the income eligibility threshold. | Is above the eligibility threshold. | The 10% Reasonable Compatibility Test is required. |
| Is below the income eligibility threshold. | Is not available. | Request additional verification/clarification. |
| Is above the income eligibility threshold. | Is above the income eligibility threshold. | Individual is ineligible. 10% Reasonable Compatibility Test is not required. Refer to the FFM. |
| Is above the income eligibility threshold. | Is below the income eligibility threshold. |
Request additional verification/clarification. |
| Is above the income eligibility threshold. | Is not available. |
Request additional verification/clarification. |
Refer to the Reasonable Compatibility Calculator within the MAGI Policy Manual, Appendix B.
Always begin by looking at the income as a whole. If total attested household income is NOT reasonably compatible with EOI, you must look at each income separately.
EXAMPLE: Marilee and Jacob are married with two children both over age one (1). They attested their combined income is $2900.00 per month. EOI shows their combined income as $3250.00 per month
When the income is entered in the Reasonable Compatibility Calculator (Appendix B) it shows that their statement of combined income is below the MHK income guideline of $3201 for a household of 4.
| Reasonable Compatibility Calculation Sheet (revised 04-01-2018) | |
|---|---|
| Date: | |
| Budget Month: | |
| Head of Household Name: | Marilee |
| DCN: | |
| Household Size: | 4 |
| Program: | MHK 1-18 |
| Income Standard for Household Size of Selected Program | 3201 |
| Monthly Self-Attested Household Modified Adjusted Gross Income (MAGI) | 2900.00 |
| Monthly Electronically Obtained Income (EOI) | 3250.00 |
| Are self-attested income and EOI both above the income standard for the selected program? | NO |
| If YES, household is ineligible for selected program. Stop here, determine if eligibility exists for any other program. If so, update program and income standard to desired program. If not, reject case or start adverse action. | |
| If NO, continue to the next question below. | |
| Are self-attested income and EOI both below the income standard for the selected program? | NO |
| If YES, income is reasonably compatible. Accept applicant/participant attestation of income and do not request further clarification of income. | |
| If NO and one income is above the income standard and one is below the income standard, compare income sources using the chart below. | |
| Income Standard for household size of selected program: | 3201 |
| Self-Attested Household MAGI: | 2900.00 |
| Electronically-Obtained Income (EOI) converted to a monthly amount: | 3250.00 |
|
Percentage Difference |
12.07% |
| Is the difference more than 10%? | YES |
| If YES, the income is not reasonably compatible. Request clarification of income. | |
| If NO, the income is reasonably compatible. Accept client attestation of income. | |
The difference in the two (2) incomes is 12.07%.
Their combined income is not reasonably compatible.
Because there are two (2) incomes it must be determined if one or both incomes are not reasonably compatible.
Separate the two incomes and enter each one in the Reasonable Compatibility Calculator. You will ONLY look at the percentage at the bottom of the calculator. Is each individual’s income at or below 10%? If so, the income for that person is reasonably compatible.
After entering each individual income, send a Request for Information (IM-31A) asking for verification of income that is not reasonably compatible. Once you receive that verification, determine if it is reasonably compatible with their original statement.
EXAMPLE (cont’d): The application shows that Marilee’s income is $500 per month. EOI shows her income as $515 per month. The difference in her attestation and the EOI is 3%. Marilee’s statement of income is reasonably compatible. No further verification is necessary.
The application shows that Jacob’s income is $2400 per month. EOI shows his income as $2735 per month. The difference in his attestation and the EOI is 13.96%. Jacob’s statement of income is NOT reasonably compatible. Request verification for Jacob’s income.
Marilee:
| Self-Attested Household MAGI: | 500.00 |
| Electronically Obtained Income (EOI) converted to a monthly amount: | 515.00 |
|
Percentage Difference |
3.00% |
| Is the difference more than 10%? | NO |
| If YES, the income is not reasonably compatible. Request clarification of income. | |
| If NO, the income is reasonably compatible. Accept client attestation of income. |
Jacob:
| Self-Attested Household MAGI: | 2400.00 |
| Electronically Obtained Income (EOI) converted to a monthly amount: | 2735.00 |
|
Percentage Difference |
13.96% |
| Is the difference more than 10%? | YES |
| If YES, the income is not reasonably compatible. Request clarification of income. | |
| If NO, the income is reasonably compatible. Accept client attestation of income. |
The following sections describe what income is included and excluded, what deductions are allowable, and applying the five percent (5%) disregard for MAGI households.
All income must be entered into MEDES.
Types of included income under MAGI methodology include but are not limited to:
NOTE: Prior to processing the eligibility determination, the following must be sent with a Request for Interpretation of Policy (IM-14) through the proper supervisory channels:
These will be reviewed by MHN Program and Policy and/or Division of Legal Services staff and the response will include a decision on whether or not the income is countable for MAGI programs.
NOTE: Supplemental Security Income (SSI) is not the same as Social Security Administration benefits (SSA). SSI is not included as income.
NOTE: Count a child’s income only when that child must file taxes on the income. The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) excludes SSA income for children until it reaches a formulaic threshold in combination with the child’s other income sources. In 2015 the threshold is $25,000 (the threshold may change annually).
The current formula for calculating taxable SSA income of a child is:
EXAMPLE: Child receives SSA of $1405 per month. The child started receiving SSA two years ago, and did not receive a lump sum during the tax year. The family was not able to provide the SSA-1099. The child has no other income.
| Determine annual SSA income | $1,405 x12 = $16,860 |
| Include the full amount of any lump-sum SSA benefit payments received in current tax year. | + zero (No lump sum received in tax year.) |
| Divide in half. | ($16,860 + 0)/2=$8,430 |
| Add any taxable pensions, wages, interest, dividends, and other taxable income. | + zero (No additional pensions, wages, interest, etc. received in tax year.) |
| Compare to $25,000 | $8,430 is under $25,000 so the child’s SSA income is EXCLUDED in MEDES. |
NOTE: Compensation in lieu of wages/bartering is defined as:
Generally, this income is reported on a Schedule C or Schedule C-EZ (Form 1040).
EXAMPLE: Applicant works at the front desk of a hotel in exchange for a room to stay in at the hotel. The applicant and the manager of the hotel agreed that the weekly rate for the hotel room was $380.00 and that the applicant was to work 40 hours per week in exchange for the room. The $380.00 is considered compensation in lieu of wages/bartering and is included as the weekly income source for the applicant.
NOTE: If there is evidence that income should not be taxable, as there are some exceptions depending on the source of the income, submit an IM-14 (Request for Interpretation of Policy) with supporting documents through proper supervisory channels.
All sources of income must be entered into MEDES including excluded income. Participant statement is acceptable for verification of excluded income, however, if an electronic data source is available, use reasonable compatibility guidelines.
Types of excluded income under MAGI methodology include:
NOTE: When a custodial parent receives money from a non-custodial parent that is not court ordered but is intended to be used to support the child(ren), enter the amount received in MEDES as child support. Enter the child support income under the child’s name or divide it equally between the children it is intended to support, who reside in the home.
EXCEPTION: Gifts and inheritances are not included, except when there is income generated from the gifts or inheritances such as rent received from property. That income is taxable and counted under MAGI methodology;
NOTE: Include as income any of the above grants available to students for current living expenses (grants - educational expenses = money available for current living expenses).
NOTE: Include as income any scholarships available to students for current living expenses (scholarships - educational expenses = money available for current living expenses).
A loan must be:
NOTE: Income contributed to an ABLE account by the owner or beneficiary him- or herself is NOT disregarded from the participant’s income.
EXAMPLE: John, age 23, receives $500 a month from a part-time job. He deposits $50 of his earnings into his own ABLE account. In this instance, his entire wage amount counts for his MAGI determination because how John spends the earnings he receives does not change its designation as taxable, countable income.
Deductions are expenses that lower taxable income. Because MAGI MO HealthNet (MHN) is based on taxable income, deductions must be incorporated in the calculation of the MAGI-based income.
Self-attestation is accepted for deductions allowed in the calculation of MAGI income. The self-attested income and deductions must be found Reasonably Compatible (RC) with electronic data sources. If the self-attested amount is not RC, additional information should be requested. If the additional information is not provided, do not deny or reject the application or case. Eligibility is determined without including the deductions.
EXAMPLE: Samuel applied for benefits on his 3 year old daughter, Mikayla. Samuel claims Mikayla as a tax dependent and is the custodial parent. Samuel attests to self-employment income of $1,500 per month. Samuel also attests to expenses related to his business: health insurance for himself of $250 per month and self-employment tax of $1,300 per year. Samuel is sent an IM-31A to provide verification of his deductions. Samuel failed to provide the required verification by the end of the IM-31A period. All other eligibility factors were met. The application is approved, however, the deductions are not allowed in the MAGI income as verification was not provided. Eligibility determination is made on Samuel’s gross income.
Pre-Tax Deductions
Pre-tax deductions are taken out of an individual’s income before any Federal, State and local taxes are deducted.
- Some health insurance premiums paid by the employee;
- This may include premiums paid for dental and vision.
- Some employee contributions to 401(k) and 403(b) retirement plans; and
- Contributions to deferred compensation plans.
- Health Savings Accounts (HSA)
Pre-tax deductions cannot be claimed on an individual’s tax return as this expense has already been excluded from the individual’s taxable income. Therefore, tax documents will not include verification of pre-tax deductions.
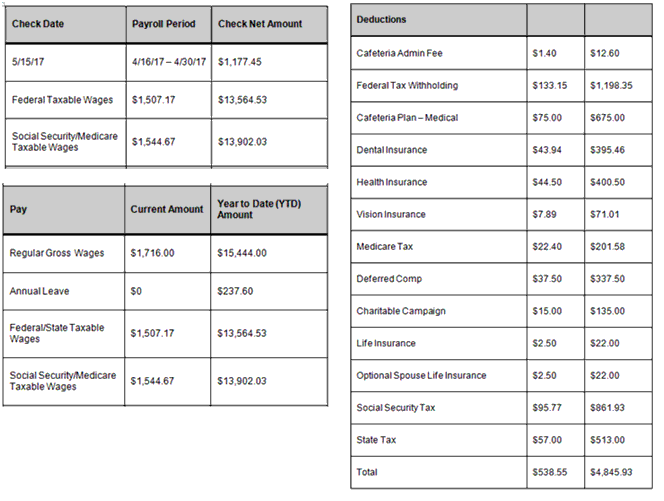
EXAMPLE: Jan is employed and is paid semi-monthly (twice per month) a salaried amount of $1,716.00. Jan’s pre-tax deductions were not RC with the electronic sources. She provided her pay stubs to verify her pre-tax deductions which include: health, vision, and dental insurance for herself, her spouse and children, and contributions to her deferred compensation plan. Jan does not claim any other deductions. To calculate Jan’s MAGI income, convert her income and deductions into monthly amounts and then subtract her deductions from her gross pay. Review Jan’s pay stub below to identify her gross pay and pre-tax deductions.

- Convert Jan’s income to reflect her monthly gross salary.
- $1,716.00 x 2 = $3,432.00
- Convert Jan’s pre-tax deductions to monthly amounts.
- Dental Insurance $43.94 x 2 = $87.88
- Health Insurance $44.50 x 2 = $89.00
- Vision Insurance $7.89 x 2 = 15.78
- Medical Cafeteria Plan $75.00 x 2 = $150.00
- Deferred Comp Contribution $37.50 x 2 = $75.00
- Total Monthly Deductions = $417.66
Outcome: Jan’s household MAGI income, after pre-tax deductions, is $3,014.34 ($3,432.00 - $417.66 = $3,014.34)
NOTE: Contributions to cafeteria plans for medical expenses are allowed as a MAGI pre-tax deduction. Cafeteria contributions are deducted from the taxable income and set aside for medical expenses incurred during that particular tax year. Only allow cafeteria plan deductions for medical expenses. Cafeteria plan contributions for child care expense are not allowed as a MAGI pre-tax deduction.
Other Allowable Income Deductions (Adjustments to Gross Income)
In addition to pre-tax deductions, MAGI allows other income deductions which are “adjustments” to the individual’s gross income. These adjustments allow certain types of expenses to be deducted from the income after taxes are paid. Meaning, income taxes have already been paid prior to incurring these expenses. These deductions are claimed as a deduction on the Federal Income Tax Return at the end of the tax year.EXAMPLE: Jon applies for MAGI Family MO HealthNet (MHN) for his 8 year old daughter, Hazel, who he expects to claim as a dependent. Jon is an elementary school teacher. His monthly gross income is $2,250. He spent $240 on supplies for his classroom (Educator Expense Deduction) in the taxable year.Hazel’s MAGI-based household size is herself and her father, Jon.
To calculate Jon’s income, and Hazel’s MAGI household income, divide the Educator Expense by 12 months ($240 / 12 = $20), and subtract that amount from the MAGI household income ($2,250 - $20 = $2,230). The monthly MAGI household income is $2,230.
These deductions can be found on IRS form 1040, lines 23-35. However, the individual does not have to file a tax return to get the deduction.
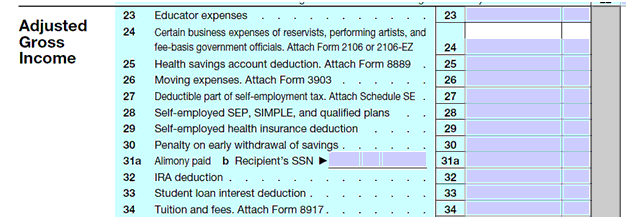
When other allowable deductions are not reported or they are unknown, make an eligibility determination without applying the deduction. Do not deny or close an application or case for verification of deductions.
Allow the following expenses as deductions from an individual’s Adjusted Gross Income:
NOTE: This is different than the HSA pre-tax deduction. This amount is based on Form 8889, not the individual’s pay stub.
NOTE: An individual may not claim this deduction if the contribution was made by someone other than their self, such as: employer contributions, rollovers, or qualified HSA funding distribution from an IRA.
NOTE: This is based on the Schedule SE (Self-Employment Tax); Section A of the Schedule SE, line 6, or Section B of the Schedule SE, line 13.
NOTE: This is based on forms; Schedule C, C-EZ, or F
NOTE: If the self-employed individual is enrolled under a spouse’s health insurance plan (or any other health insurance plan other than under the business), do not use the amount paid for health insurance.
NOTE: This does not include contributions to Roth IRAs.
NOTE: A student loan is not considered qualified when: 1) any of the proceeds of the loan were used for purposes other than the qualified higher education expenses, 2) the loan proceeds were borrowed from a relative, or 3) the loan proceeds were borrowed from a qualified employer plan.
NOTE: For an individual to qualify as attending an eligible education institution, they must receive Form 1098-T from the education institution.
Deductions may exceed the MAGI based household income. When this occurs, the MAGI household income would be less than zero. To determine financial eligibility, use $0 as the MAGI household income.
NOTE: Income and deductions should be entered as reported by the individual. Allow the system to calculate the $0 budget; do not manually enter a $0 budget.
A component of MAGI methodology, the five percent (5%) disregard, is introduced in 42 CFR 435.603(d)(1). The five percent (5%) disregard replaces earned income disregards previously used to determine eligibility for the Family MO HealthNet programs.
The income disregard equals five percent (5%) of the Federal Poverty Level (FPL) for the household size. The five percent (5%) disregard is added to the income standard for the program based on household size, when an individual would be determined eligible if the FPL income standard was five percent (5%) higher. This disregard applies to the following programs:
MO HealthNet for Families (MHF) eligibility is not based upon a percentage of federal poverty level. The income standard for MHF is a dollar amount based upon the July 16, 1996 Aid to Families with Dependent Children (AFDC) standard converted to a MAGI based standard. To determine the five percent income disregard for MHF, 5% of 100% of the FPL is added to the MHF income standard.
The resulting figure is always rounded up to the benefit of the participant.
EXAMPLE 1: Mr. Jones is applying for CHIP on behalf of his two children. He files taxes and claims both children as dependents. The household composition for each child is the same as the tax filer’s, and consists of Mr. Jones, Child 1, and Child 2. Mr. Jones is employed and earns $30.00 per hour working 40 hours per week or $5199.60 per month ($30.00 x 40= $1,200.00 x 4.333).
Mr. Jones’ income |
$5,199.60 per month |
CHIP 75 income maximum (300% FPL) |
$5,195 per month |
In this example it appears the children are not eligible for any coverage as the household income is above $5,195.00 (300%) per month. However, Mr. Jones’s income is barely above the limit for CHIP coverage, so the 5% disregard may make a difference in the level of care.
In order to calculate the 5% disregard you will need to know that 100% of the annual federal poverty level for a household of three is $20,780.00.
To determine the CHIP 75 income level including the 5% disregard:
Since Mr. Jones’ income of $5,199.60 per month is below $5,2282.00 (305% of FPL) his children are eligible for CHIP 75 level of care. He will have a premium to pay.
EXAMPLE 2:Mr. Brown is applying for MO HealthNet for Kids (MHK) for his three children all over the age of six. Mr. Brown files taxes and claims the three children as dependents. The household composition for each child is the same as the tax filer, and consists of Mr. Brown, Child 1, Child 2, and Child 3. Mr. Brown is employed and earns $3,200 per month.
Mr. Brown’s income |
$3,200 per month |
CHIP 71 or 72 income maximum (150% FPL/non-premium) |
$3,138 per month |
CHIP 73 income maximum (185% FPL/premium) |
$3,870 per month |
(CHIP 71 is for children ages 1-5; CHIP 72 is for children ages 6-18)
In this example it appears the children are not eligible for a non-premium level of care as the income maximum for non-premium CHIP coverage is $3,138.00 per month. However, Mr. Brown’s income is barely above the limit for non-premium CHIP 71 or 72 coverage, so the 5% disregard may make a difference in the level of care.
In order to calculate the 5% disregard you will need to know that 100% of the annual federal poverty level for a household of four is $25,100.00.
To determine the CHIP 71 or 72 income level including the 5% disregard:
Since Mr. Brown’s income of $3,200 per month is below $3,243 (155% of FPL) his children are eligible for CHIP 72 level of care (all over the age of six) and he will not need to pay a premium.
EXAMPLE 3: Mrs. Smith is applying for MO HealthNet for Families (MHF) for herself and her six children. Mrs. Smith does not file taxes. Mrs. Smith’s household composition is herself and her six children. Her income is $519 per month.
Mrs. Smith’s income |
$519 per month |
MHF income maximum |
$490 per month |
MHK POV income maximum (above MHF/up to 148%) |
$4,695 per month |
In this example it appears Mrs. Smith and her children are not eligible for MHF coverage as the income maximum for MHF is $490 per month. However, Mrs. Smith’s income is barely above the limit for MHF coverage, so the 5% disregard may make a difference in the level of care.
In order to calculate the 5% disregard you will need to know that 100% of the annual federal poverty level for a household of seven is $38.060.00.
To determine the MHF income level including the 5% disregard:
Since Mrs. Smith’s income of $519.00 per month is below $649.00 (MHF standard plus 5% of FPL) she and her children are eligible for MHF level of care.
In determining eligibility based on MAGI methodology, use the following calculations:
| Total adjusted gross income (earned and unearned income) | |
| PLUS | Foreign earned income, tax-exempt interest, or tax-exempt Social Security income |
| MINUS | Allowable deductions |
| EQUALS | Modified Adjusted Gross Income (MAGI) |
In determining eligibility based on MAGI methodology, use the following calculations:
| Total adjusted gross income (earned and unearned income) | |
| PLUS | Foreign earned income, tax-exempt interest, or tax-exempt Social Security income |
| MINUS | Allowable deductions |
| EQUALS | Modified Adjusted Gross Income (MAGI) |
NOTE: See sections on included income, excluded income, and allowable deductions for examples.
The Modified Adjusted Gross Income (MAGI) is then compared to income guidelines for the specific program. Refer to Appendix A in the Family Healthcare Manual (MAGI) for
the MAGI Income with 5% of FPL included chart.
Determine the amount of earned income the family will receive in present and future months. Discuss employment with them, including:
Obtain an accurate account of the participant's employment. Use the past thirty (30) days to evaluate income stability in determining how to anticipate future income and whether to average income over a longer period.
Once the individual's employment situation is determined, budget projected monthly income. Use the following guidelines to determine a monthly income amount.
If income received is other than monthly, convert it to a monthly amount:
When able to predict that the employment situation will not vary, such as a salaried employee, budget the monthly amount. Infrequent and unpredictable overtime or conversely, infrequent and unpredictable workdays missed; do not alter the certainty of the employment situation.
When an employee's income varies from pay period to pay period, determine the likely pattern of future income to calculate a monthly average. Use past patterns of income if these patterns will continue.
When evaluating the length of time to use in determining patterns of income for projecting future income, always consider information from at least the past 30 days. If income fluctuates to the extent that a 30-day period does not provide an accurate indication of projected income, choose a different period that provides a more accurate indication of future income. Using a two-month time-period is recommended if no reason exists why a shorter or longer period would better predict future monthly income. Use a longer or shorter period if adequate for determining monthly income. Record the basis for the time-period used.
In some situations, recent past earnings records serve only as a partial guide for determining monthly income. For example, the employee or employer indicates that a change in hourly wage rates, hours of work, job responsibilities, etc., recently occurred or is imminent.
In other situations such as new employment, no recent past earnings records exist to use as a guide. In these situations, carefully evaluate the information available from the employee, in comparison with known past earnings records and work patterns, if any, to determine a monthly income amount. It may be necessary to set a priority to verify accuracy of monthly income.
When unearned income fluctuates, compute it on an annual or other representative period and convert it to a monthly amount.
Projection of income is an estimate of income that is expected to continue through the certification period. This estimate is based on expectation and knowledge of the participant's current, past, or future circumstances. In estimating the amount of included income, consider all factors that most accurately estimate and reflect the amount received.
Use current monthly income to evaluate eligibility for MO HealthNet . Current monthly income is an average of income received within the past 30 days.
If income fluctuates to the extent that a 30-day period does not accurately reflect projected income, choose a method that accurately indicates or reflects future income. Enter a detailed comment to record the reason for the time-period used.
EXAMPLE: Ms. Johnson works as a clerk in an insurance firm. Her regular hourly rate is $10.00. However, for the past four months she has been working overtime during each weekly pay period. Her gross weekly earnings with overtime is $460. Convert this to monthly income by multiplying $460 x 4.333 = $1993.18. Ms. Johnson's projected monthly income is $1993.18. Since she has been working overtime consistently for over 30 days it is appropriate to include the overtime in her budget.
EXAMPLE: Two months after approval, Ms. Johnson reports she is no longer working overtime. Complete the budget based on Ms. Johnson's normal wages of $10.00 per hour for 40 hours per week. Convert her income to monthly,$10.00 x 40 hours = $400 x 4.333 weeks = $1,733.20. Ms. Johnson's expected monthly income amount is now $1,733.20.
EXAMPLE: Ms. Smith has worked at the local factory for the past three years doing piece work. She regularly works 40 hours per week. Her income varies from pay period to pay period depending on her production. No changes are expected in the piece work rate Ms. Smith is paid, nor in the hours worked. After discussing with Ms. Smith variations in her earnings over the past several months, the most recent 30 days are not an adequate representation of her earnings. After evaluating information provided by Ms. Smith, the past 12 weeks yield the most accurate estimate of her average earnings. Total earnings for this period are $1,200, averaging $100 per week. Convert this to monthly income of 4.333 x $100 = $433.33. Project $433.33 as the monthly earnings on the budget.
"Actual income" is the income that was actually received in a particular month. Actual income is not considered a projection of income or used for ongoing projection of income. In the following situations actual income is used:
Claims that are established based on the projection of income are because one of the following applies:
Always record a comment regarding the projections of income. The comment should include what was used to determine the projected income, why it was used, how it was calculated, and any other pertinent information.
A pattern of income is used to indicate or predict future income. Income patterns are typically identified as consistent and reoccurring.
When determining income eligibility, it may be necessary to convert the income to a monthly amount. Some income pattern types and conversions are:
In some instances the pattern of income cannot be determined. This occurs when the income amount and pattern varies, with no consistency. In this situation use the past income to determine future earnings.
EXAMPLE: George sells scrap metal as his source of income. George attests he sold metal in May for $600, July for $150, and December for $400. George states he does not plan to sell anymore for the remainder of the year. Add together all that George has sold ($600 + $150 + 400 = $1,150) and average it for a monthly amount ($1,150 / 12 = $95.83 per month).
EXAMPLE: Sue works through a temp agency. She works various jobs as assigned therefore her monthly income is not consistent. She applied in November. In August she earned $1,300, September $150, October $700. Sue indicates that she is unsure of her future earnings however she plans to continue working for the temp agency. Average the previous three months to project future monthly earnings ($1,300 + $150 + $700 = $2,150 ) ($2,150 / 3 = $716.66). Her projected monthly average is $716.66.
To determine how much pay history to use for individuals whose income is inconsistent it is important to ask why the income is inconsistent and if they anticipate any changes. Gather as much information as possible to make an accurate determination of ongoing income. Record a detailed comment explaining how the pattern and calculation of income was determined.
Use the rules in this section for the specified types of income.
Comments must be entered in the Missouri Eligibility Determination and Enrollment System (MEDES) detailing how the income was verified. Comments should be placed on the Application or Integrated Case under Evidence. Click on the green action arrow for the specific evidence you are verifying and select “EDIT”.
Record any information regarding income source, reason ended, or any information pertinent to your calculation of income that requires further explanation. Include percentage for reasonable compatibility (if appropriate). Record any information regarding the income amount and how that was determined.
This statute does not make the assignment of medical support mandatory for children eligible under the CHIP premium groups such as CHIP 73, 74 or 75, MPW, or SMHB. For MPW and SMHB cases, once the child is born cooperation in pursuit of medical support is required.
The parent or caretaker must cooperate with the Family Support Division-Child Support (FSD-CS) in the pursuit of medical support, unless there is good cause for refusing to cooperate. Provide the parent/caretaker with the Referral/Information for Child Support Services (CS-201). The parent/caretaker must complete and return the CS-201 or call the Eligibility Specialist to provide the non-custodial parent’s information.
NOTE: The Notice of Requirement to Cooperate and Right to Claim Good Cause for Refusal to Cooperate in Child Support Enforcement (IM-2E Part 1) is no longer needed as the Rights and Responsibilities page of the IM-1SSL covers the information.
If the parent/caretaker claims good cause, provide the Second Notice of Right to Claim Good Cause for Refusal to Cooperate in Child Support Enforcement (IM-2E Part 2).
NOTE: If good cause is claimed and acceptable the parent/caretaker does not have to cooperate in seeking medical support.
When a child is added to an active MO HealthNet case, submit a CS-201 to FSD-CS even if the child has the same non-custodial parent as another child who is already active on the case. Use the CS-201 to inform FSD-CS of the addition of the child and any new information on the non-custodial parent.
The following steps should be taken prior to referring a MO HealthNet case to FSD-CS when a child is deprived of parental support due to the continued absence of the child's parent/s from the home.
A parent or caretaker must complete a Referral/Information for Child Support Services (CS-201) form, but the form is not required prior to approval of the MO HealthNet case. Do not hold an application pending completion of the CS-201.
EXCEPTIONS: Do not refer to FSD-CS when:
If the MO HealthNet application is made in-person, staff must have the CS-201 completed by the applicant.
If the MO HealthNet application was completed on-line, by telephone, or by mail, the CS-201 may be:
NOTE: If completed by telephone call send the CS-201 to FSD-CS and note the information was obtained by telephone in the signature section along with the date of the call.
If unable to contact applicant by telephone, mail a Request for Information (IM-31A) allowing 10 days for the applicant to complete and return the form.
The applicant should provide as much information as possible on the CS-201. However, if the CS-201 is not returned or returned incomplete, FSD staff must fill out the form with at least the following information:
NOTE: The applicant's signature is not necessary on the CS-201 for opening the child support case. FSD-CS Intake Center staff has been advised to go ahead and open the case without the signature. Do not hold up sending the document or do anything different due to the lack of a signature.
NOTE: The FSD must approve the MO HealthNet case before the CS-201 is sent. If MO HealthNet coverage is denied, the CS-201 is sent to the virtual file room. If the parent still wishes to receive Child Support services he/she may apply on-line at dss.mo.gov or request the appropriate form by calling the Child Support Call Center at (866) 313-9960.
For all completed CS-201 forms where all parties can be identified (including custodial, non-custodial/alleged parent, and children), please scan and email to:
For all completed CS-201 forms where the non-custodial/alleged parent is “unknown” and cannot be identified, please scan and email to:
All forms may also be submitted:
The Notice of Requirement to Cooperate and Right to Claim Good Cause for Refusal to Cooperate with Child Support (IM-2E Part One) contain the information that the applicant or participant must be given before being requested to cooperate. Each applicant or participant required to assign medical support rights must signify understanding of the right to claim good cause by completing the form at the time of application.
When adding a child to an active case, the applicant participant signs another copy of IM-2E Part One. This reminds the applicant or participant that he/she may claim good cause.
The Second Notice of Right to Claim Good Cause for Refusal to Cooperate with Child Support (IM-2E Part Two) contains the additional information that the applicant or participant must be given when requested or when he/she claims good cause for refusal to cooperate. The form provides space for the applicant or participant to make a good cause claim in writing. The applicant or participant and the eligibility specialist must sign and date the form.
The applicant or participant is responsible for providing all information available concerning identification of the non-custodial parent of the child for whom benefits have been requested. If the non-custodial parent's identity is unknown, the applicant or participant is responsible for providing all possible sources of information to be used in identifying the parent.
If the applicant or participant states that the non-custodial parent is unknown, explore the circumstances surrounding the claim thoroughly, and record a comment in FAMIS about the applicant or TA participant's explanation. Ask him/her to submit all information available to verify the claim. Acceptable methods of verification include:
If more than one alleged father exists for a child, or if responsibility for medical support is unclear, refer each alleged parent of that child to the Family Support Division - Child Support (FSD-CS). Complete CS-201 for each alleged parent. In cases where someone other than the legal father is alleged to be the biological father, complete a CS-201 for the legal father and one for the alleged biological father.
When children have been adopted eligibility is determined based on the adoptive parent. Complete a CS-201 when there is a non-custodial adoptive parent.
In all cases explain to the applicant or participant the importance of cooperating with the identification of the non-custodial parent. A refusal to do this may result in a determination of failure to cooperate and the application of a sanction if the participant fails to claim good cause.
The earlier paternity and/or support are established the sooner the child may:
The applicant or participant is responsible for furnishing information to help locate the non-custodial parent. If the location is unknown, the applicant or participant will be asked to provide information that may lead to possible sources for obtaining this information. Assist the applicant or participant to complete the necessary information on the CS-201. The applicant or participant's failure to participate in locating the non-custodial parent without good cause may result in a determination of refusal to cooperate and the application of a sanction.
The applicant or participant may be asked to take a more active role in identifying and locating the non-custodial parent. This may include:
Do not deny, delay, or discontinue assistance pending a determination of good cause for refusal to cooperate. When possible, make this determination before case approval. At the time of approval complete a Referral/Information for Services (CS-201) on the non-custodial parent if a final determination of good cause is pending. Inform the child support specialist (CSS) that the applicant or participant claimed good cause and that the final determination is pending.
If an applicant or participant refuses to cooperate, discuss his/her reasons. An applicant or participant may refuse to cooperate in establishing paternity or obtaining child support without sanction if good cause exists.
Good cause for refusing to cooperate exists when one or more of the following circumstances exist:
EXCEPTION: The Family Support Division will pay for an evaluation from a mental health professional regarding risk of emotional harm when necessary. The applicant or participant's inability to pay a fee will not negatively affect a determination that good cause exists.
NOTE: If a participant notifies Income Maintenance in the future that good cause no longer exists, it is necessary to complete a new CS-201 or send an IM-16 notifying FSD-CS that they can reopen the child support case.
Evidence to support a good cause claim may include the following:
Types of Evidence:
When documentation is unavailable, accept statements of the child, applicant, or participant. The applicant or participant is responsible for providing enough information to establish good cause and explain why no evidence is available. Make efforts to corroborate the statements by someone familiar with the situation
Types of Evidence:
These records may include a written statement from the applicant or participant if formal documentation is not available.
Types of Evidence:
Types of Evidence:
Types of Evidence:
NOTE: If the applicant or participant needs a mental evaluation to prove emotional harm, the evaluation is paid the same as an examination to determine incapacity. The evaluation is valid for two years unless the mental health professional or Income Maintenance staff determines that another evaluation is needed.
Additional evidence may be requested when evidence provided by the applicant or participant does not provide enough information to make a good cause determination.
NOTE: DO NOT CONTACT THE NONCUSTODIAL PARENT UNDER ANY CIRCUMSTANCES.
When an individual fails to cooperate with Child Support (CS) in obtaining medical support and good cause does not exist, the individual is sanctioned. Sanctioning an individual ends his/her MO HealthNet (MHN) coverage.
NOTE: Only parents and caretakers can be sanctioned. Do not sanction children.
CS determines if the individual has cooperated or if a sanction should be imposed. If a sanction should be imposed, CS will notify the Family Support Division (FSD). If good cause does not exist, FSD sanctions the individual.
NOTE: FSD determines if good cause exists; refer to 1805.040.10.15.05 Determining Good Cause.
FSD-CS will use the email address FSD.GROUPC@dss.mo.gov when sending a request to enter MO HealthNet sanction due to non-cooperation in pursuit of medical support, or to end a sanction when the individual cooperates with CS.
Emails received from CS requesting entry or ending of a child support sanction will contain “Child Support Sanction" in the subject line. Income Maintenance (IM) must act on the sanction request within ten (10) days of receipt of the request.
NOTE: When an individual cooperates, CS sends a request to FSD to lift a sanction. CS will send an email advising FSD that the individual is now eligible to receive benefits. Follow appropriate procedures to end the sanction and reactivate the caretaker’s MO HealthNet benefits, if they remain otherwise eligible, within ten (10) days.
MAGI Processing Centers must have a process to identify and distribute these email messages to appropriate staff, and to ensure action requested by CS is taken within ten (10) days.
Follow adverse action procedures prior to imposing the sanction. If a hearing is requested within the adverse action period:
When a child is added to an active MO HealthNet case submit a CS-201 to FSD-CS even if the child has the same non-custodial parent as another child who is already active on the case. Use the CS-201 to inform FSD-CS of the addition of the child and any new information on the non-custodial parent.
It is a requirement to complete and return the CS-201, or the parent/caretaker must call the eligibility specialist to provide the non-custodial parent information. Even if the parent/caretaker fails to provide the necessary information on the non-custodial parent, add the child to the case. Refer to section 1805.040.10.20 for sanctioning procedures.
RSMo 208.151.1 effective August 28, 2013, allows certain individuals under the age of 26 who were in foster care to be eligible for healthcare coverage through the Children's Division (CD).
To qualify, a person must:
If the applicant is eligible for coverage through FSD and they are currently receiving former foster care youth coverage (ME 38) through the Children’s Division, do not reject the application. Send an email, with a subject line of AC ME 38 - NEEDS TO BE CLOSED to Cole.MHNPolicy@dss.mo.gov. Include:
NOTE: FSD staff must approve MO HealthNet coverage the day that the former foster care coverage shows as closed in MXIX. Due to the overnight batch process and to prevent gaps in coverage, CD will NOT close ME 38 coverage before a weekend or holiday. Requests received on these days will be processed on the following business day.
If the former foster care individual has been determined ineligible for a full coverage Family MO HealthNet or MO HealthNet for the Aged, Blind or Disabled program through FSD, refer the individual to CD for coverage.
NOTE: To allow for continuity of coverage for former foster care individuals, CD currently auto-enrolls participants in Former Foster Care Youth coverage at the time of age-out, however, a gap in coverage may exist.
EXAMPLE: Mr. Carson was given Former Foster Care Youth coverage when he turned 18. At age 20, he moved out of Missouri to attend college in Iowa and his coverage was closed. When he graduated at age 22, Mr. Carson moved back to Missouri, but did not notify CD to have his former foster care youth coverage reopened. He applied for MO HealthNet for Families coverage, but he had too much income to qualify. His case was then referred to CD to have his former foster care youth coverage reopened.
Uninsured Women’s Health Services (UWHS) or Extended Women’s Health Services (EWHS) do not provide full MO HealthNet benefits. When an applicant/participant is eligible for either of these programs, she must be referred for full healthcare coverage through CD.
NOTE: Current system functionality provides qualifying participants with Former Foster Care Youth coverage whenever other FSD coverage is ended without further action by FSD staff. However if the participant failed to report an address change to CD while receiving health coverage, the Former Foster Care Youth coverage will not be automatically reinstated.
EXAMPLE: Ms. O’Brien has active Former Foster Care Youth coverage when she applies for MO HealthNet for Pregnant Women (MPW) and is found eligible. Since the participant must be given full coverage through FSD if eligible, the Eligibility Specialist (ES) sends an email to Cole.MHNPolicy@dss.mo.gov to have the AC ME 38 closed. Once the Former Foster Care Youth coverage is closed, the ES approves the MPW coverage.
After the MPW coverage has ended and before the MPW post-partum coverage has ended, the participant should be given an ex parte review to determine whether or not she meets the eligibility criteria for a full coverage FSD MO HealthNet program. Ms. O’Brien is eligible for EWHS, which is not a full coverage program. The ES takes action to prevent the EWHS coverage from beginning and when the MPW post-partum coverage ends in MEDES, the Former Foster Care Youth coverage will begin automatically preventing a gap in full medical coverage.
If a former foster care individual has been determined ineligible for a Family MO HealthNet full coverage program through FSD, the Eligibility Specialist (ES) will send an email to Cole.MHNPolicy@dss.mo.gov so that the individual may be referred to the CD for coverage as eligibility for the Former Foster Care Youth program may exist.
Individuals who qualify for former foster care youth coverage may also contact the MO HealthNet open enrollment broker by telephone to 800-348-6627, or Children's Division at http://dss.mo.gov/cd/ or by telephone to 573-522-8024.